【浅水流方程式】Roe法でダム崩壊問題を解いてみました(wet bedとdry bed) 動画とC++コード付き
【浅水流方程式】サイトマップ(ここから関連記事が探せます)
http://mathlang.hatenablog.com/entry/2018/12/18/213650
今回は、Roe法を用いてダム崩壊問題(dam break problem)を解いてみました。Roe法とは、ヤコビアンを固有値の正負によって分割し、Roe平均(Roe average)と呼ばれる特別な平均を用いてそれらを評価し、正負に合わせて風上化をかける手法です。解いている方程式は、摩擦、勾配なしの1次元浅水流方程式(Shallow Water Equations)です。
初期状態としては、wet bedの場合は、領域のちょうど左側で水深が1.0、領域のちょうど右側で水深が0.1で、水面は静止しているものとします。dry bedの場合は、領域のちょうど左側で水深が1.0、領域のちょうど右側で水深が で、水面は静止しているものとします。このように、dry bedの場合は非常に小さい水深を与えることとします。時刻
に真ん中にあるしきり(ダム)を取り去った時に、水がどのように動くかを計算します。境界条件としては右端、左端で水深、流量ともに斉次のノイマン条件を課しています。
参考文献としてはToroの"Shock-Capturing Methods for Free-Surface Shallow Flows"のpp.187-191です。

Shock-Capturing Methods for Free-Surface Shallow Flows
- 作者: Eleuterio F. Toro
- 出版社/メーカー: Wiley
- 発売日: 2001/03/23
- メディア: ハードカバー
- この商品を含むブログを見る
こちらがwet bedの場合の計算結果です。水深が青い線で表示されています。
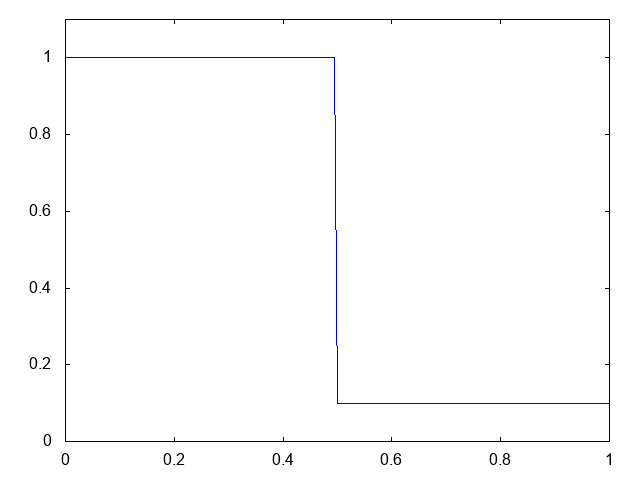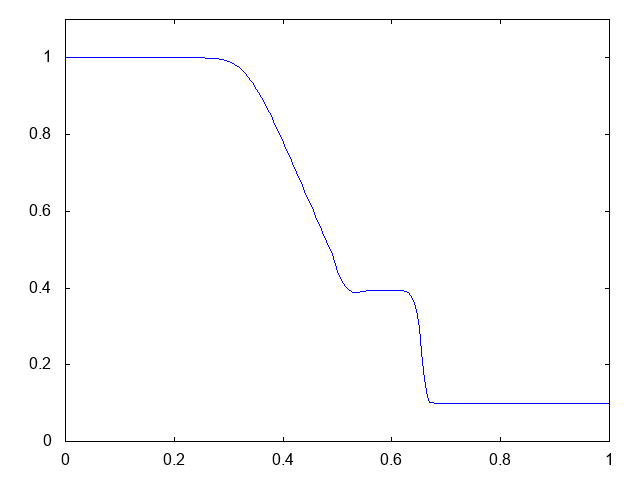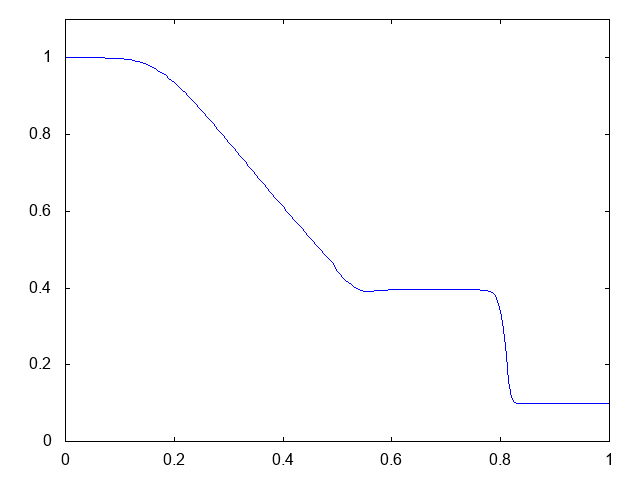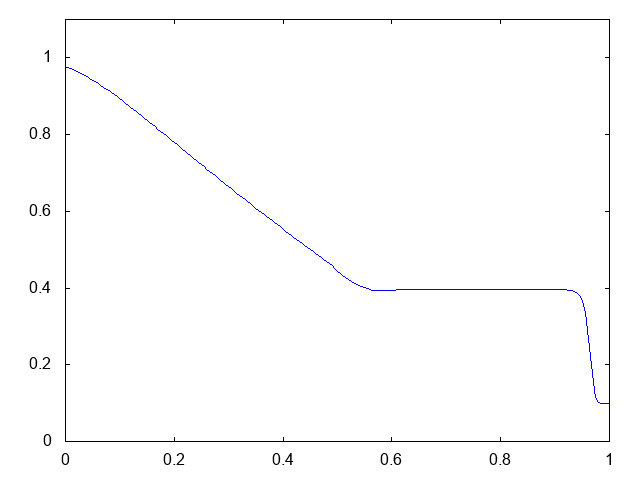
右へと進行する衝撃波(不連続な波、Shock wave)と左へと進行する膨張波(連続な波、Rarefaction wave)が観察できます。よい感じです。
こちらがdry bedの場合の計算結果です。
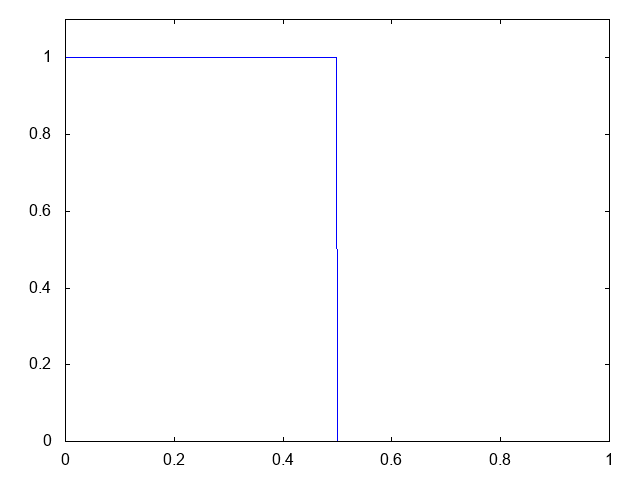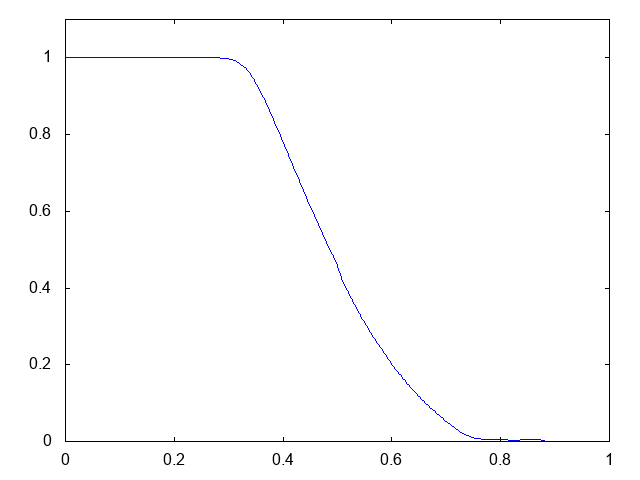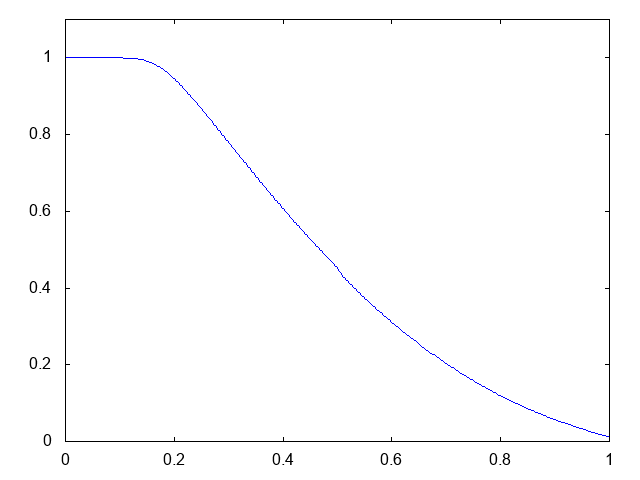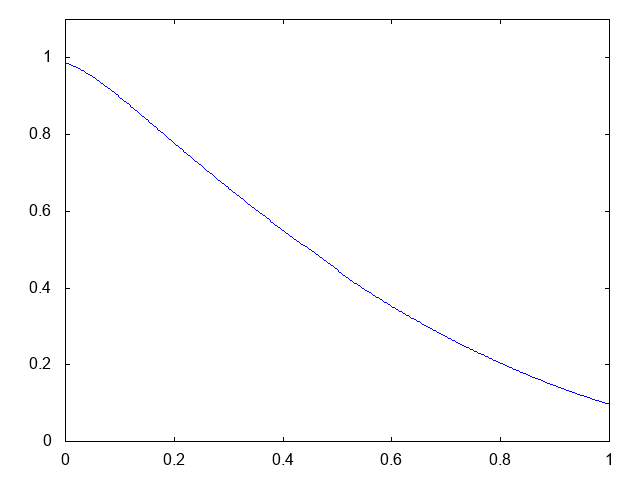
右へと進行する膨張波(連続な波、Rarefaction wave)が観察できます。よい感じです。しかしHLL法と比べて小さい水深がとれません。また、やはり膨張波は苦手のようです。
では計算コードです。
#include <iostream> #include <cmath> #include <fstream> #include <iomanip> #include <sstream> using namespace std; const double g=9.8; //celerity// inline double a(double h) { return sqrt(g*h); } //flux for continuity equation// inline double Fluxcon(double h, double q) { return q; } //flux for momentum equation// inline double Fluxmom(double h, double q) { return q*q/h+g*h*h/2.0; } //Roe average for h double Roeh(double hL, double hR) { return sqrt(hL*hR); } //Roe average for q double Roeq(double hL, double hR, double qL, double qR) { return (sqrt(hL)*qL+sqrt(hR)*qR)/(sqrt(hL)+sqrt(hR)); } //Roe flux// inline void RoeFlux(double FLR[], double hL, double hR, double qL, double qR) { double rh=Roeh(hL,hR); double rq=Roeq(hL,hR,qL,qR); double lamp=rq/rh+a(rh);//plus double lamm=rq/rh-a(rh);//minus double lampR=qR/hR+a(hR); double lampL=qL/hL+a(hL); double lammR=qR/hR-a(hR); double lammL=qL/hL-a(hL); //entropy fix, Chakravarthy// if((lampL<0.0)&&(0.0<lampR)) lamp=lamp/abs(lamp)*(abs(lamp)+(lampR-lampL)/2.0); if((lammL<0.0)&&(0.0<lammR)) lamm=lamm/abs(lamm)*(abs(lamm)+(lammR-lammL)/2.0); double M11=(lamp*abs(lamm)-abs(lamp)*lamm)/(2.0*sqrt(g*rh)); double M12=(abs(lamp)-abs(lamm))/(2.0*sqrt(g*rh)); double M21=(lamp*lamm*(abs(lamm)-abs(lamp)))/(2.0*sqrt(g*rh)); double M22=(abs(lamp)*lamp-abs(lamm)*lamm)/(2.0*sqrt(g*rh)); double dh=hR-hL; double dq=qR-qL; FLR[0]=(Fluxcon(hR,qR)+Fluxcon(hL,qL)-(M11*dh+M12*dq))/2.0; FLR[1]=(Fluxmom(hR,qR)+Fluxmom(hL,qL)-(M21*dh+M22*dq))/2.0; } inline void output(double h[], double z[], int Node, double dx) { stringstream ss; string name; ofstream fo; static int count=0; ss<<count; name=ss.str(); name="h_" + name + ".txt"; fo.open(name.c_str ()); for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { fo<<dx*float(i)<<" "<<h[i]+z[i]<<endl; } fo<<endl; fo<<endl; for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { fo<<dx*float(i)<<" "<<z[i]<<endl; } count+=1; } int main() { const int n=200;//number of cells const int Node=n+1; double L=1.0; double dx=L/double(n); double dt=0.0001; double TotalTime=0.15; int div=20;//for output double q[Node]; double h[Node]; double qn[Node]; double hn[Node]; double FL[2],FR[2]; double InithL=1.0; double InithR=0.1; double z[Node]; double I[Node]; double mn=0.01; //IC// for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { q[i]=0.0; h[i]=InithL; } for(int i=Node/2;i<Node;i++) { q[i]=0.0; h[i]=InithR; } //bottom// for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { z[i]=0.0; double a=0.5-20.0*(float(i)*dx-0.5)*(float(i)*dx-0.5); if(a>0.0) z[i]=a; z[i]=0.0; } //slope// for(int i=1;i<Node-1;i++) { I[i]=-(z[i]-z[i-1])/dx; } //at boundary// I[0]=-(z[1]-z[0])/dx; I[Node-1]=-(z[Node-1]-z[Node-2])/dx; //IC output// output(h,z,Node,dx); //time step// for(int k=1;double(k)*dt<=TotalTime;k++) { //inner cells// for(int i=1;i<Node-1;i++) { //left flux, between i-1 and i// RoeFlux(FL,h[i-1],h[i],q[i-1],q[i]); //right flux, between i and i+1// RoeFlux(FR,h[i],h[i+1],q[i],q[i+1]); hn[i]=h[i]-dt/dx*(FR[0]-FL[0]); qn[i]=q[i]-dt/dx*(FR[1]-FL[1]);//+dt*g*h[i]*(I[i]-mn*mn*q[i]*abs(q[i])/pow(h[i],10.0/3.0)); } //BC// //left boundary// hn[0]=hn[1]; qn[0]=qn[1]; //right boundary// hn[Node-1]=hn[Node-2]; qn[Node-1]=qn[Node-2]; //update// for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { q[i]=qn[i]; h[i]=hn[i]; } //output// if(k%div==0) { output(h,z,Node,dx); cout<<"t="<<double(k)*dt<<endl; } } return 0; }
こちらもどうぞ
【数物リンク】Roe法の解説資料まとめ
浅水流方程式に対する数値計算手法であるRoe法の日本語で読める解説資料まとめです。Roe法は"Flux Difference Splitting"(FDS)とも呼ばれています。
http://www.astro.phys.s.chiba-u.ac.jp/netlab/summer-school_2004/TEXTBOOK/text2.pdf
http://redmagic.i.hosei.ac.jp/~matsu/konan15/book.pdf
p.10にエントロピー補正(entrropy fix)のまとめあり。Chakravarthy の修正法がおすすめ。
http://www.astro.phys.s.chiba-u.ac.jp/netlab/mhd_summer2001/roe.pdf
http://www.icehap.chiba-u.jp/activity/SS2015/textbook/miyoshiSS2015new2.pdf
9.3
http://www2.yukawa.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~akira.mizuta/Mizuta_lecture2_euc_v4.pdf
3.3
http://www.nagare.or.jp/download/noauth.html?d=34-2tokubetu2.pdf&dir=85
http://th.nao.ac.jp/MEMBER/tomisaka/Lecture_Notes/Fluid_dynamics/Summer_School/1.pdf
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jscej1984/2001/670/2001_670_25/_pdf/-char/ja
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/prohe1990/45/0/45_0_895/_pdf/-char/en
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jscej1984/2002/705/2002_705_31/_pdf/-char/ja
http://kane-please.hatenablog.com/entry/2018/12/05/195007
http://www.jspf.or.jp/Journal/PDF_JSPF/jspf2007_03/jspf2007_03-228.pdf
http://center.stelab.nagoya-u.ac.jp/summer-school/pdf/text1-3.pdf
http://www.hepl.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/thesis/bachelor/14miyazaki_thesis.pdf
【浅水流方程式】HLL法で周期境界条件の場合のダム崩壊問題を解きます 動画とC++コード付き
【浅水流方程式】サイトマップ(ここから関連記事が探せます)
http://mathlang.hatenablog.com/entry/2018/12/18/213650
今回は、HLL法(Harten, Lax, van Leer法)を用いて周期境界条件でダム崩壊問題を解いてみました。解いている方程式は、摩擦、勾配を無視した1次元浅水流方程式(Shallow Water Equations)です。
領域の真ん中だけちょっと水位が高くなっています。境界条件は周期境界条件、すなわち右端と左端がつながっています。
参考文献としてはToroの"Shock-Capturing Methods for Free-Surface Shallow Flows"のpp.179-181です。まさにバイブルです。波速を推定するための手法としては、Exact Depth Positivity Riemann Solver (EDPRS)、Two-Rarefaction Riemann Solver (TRRS)、Two-Shock Riemann Solver (TSRS) を選べるようになっています。

Shock-Capturing Methods for Free-Surface Shallow Flows
- 作者: Eleuterio F. Toro
- 出版社/メーカー: Wiley
- 発売日: 2001/03/23
- メディア: ハードカバー
- この商品を含むブログを見る
こちらが計算結果です。青い線が水深です。
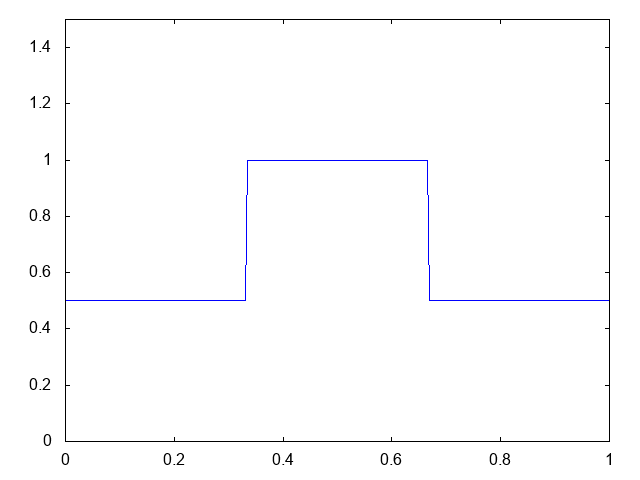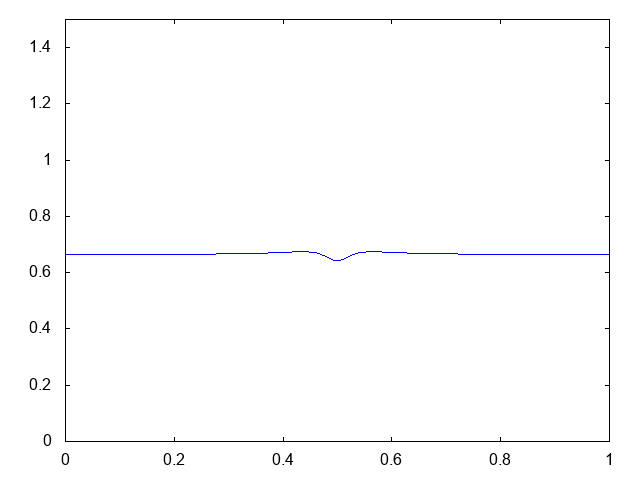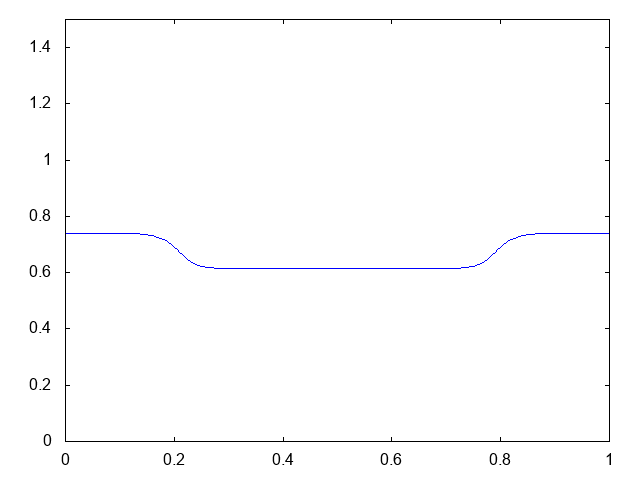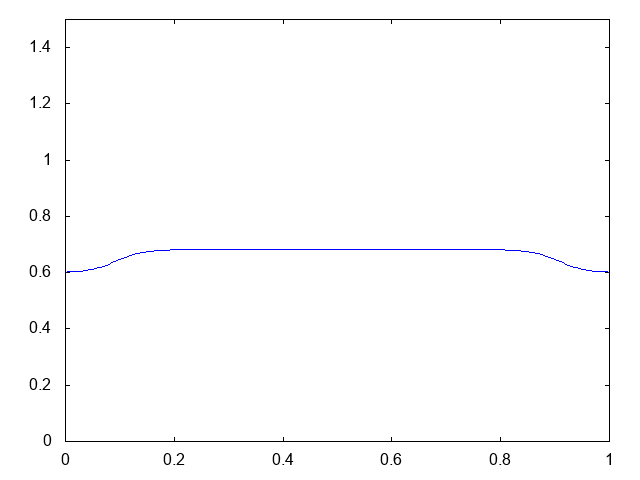
では計算コードです。BCに注目。
#include <iostream> #include <cmath> #include <fstream> #include <iomanip> #include <sstream> using namespace std; const double g=9.8; //celerity// inline double a(double h) { return sqrt(g*h); } //function for TRRS// inline double gk(double h0, double hlr) { return sqrt(g/2.0*(h0+hlr)/(h0*hlr)); } //Riemann Solver Based on Exact Depth Positivity// inline void EDPRS(double &hst, double &ust, double hL, double hR, double qL, double qR) { double aL=a(hL); double aR=a(hR); double uL=qL/hL; double uR=qR/hR; hst=(hL+hR)/2.0-(uR-uL)*(hL+hR)/4.0/(aL+aR); ust=(uL+uR)/2.0-(hR-hL)*(aL+aR)/(hL+hR); } //Two-Rarefaction Riemann Solver// inline void TRRS(double &hst, double &ust, double hL, double hR, double qL, double qR) { double aL=a(hL); double aR=a(hR); double uL=qL/hL; double uR=qR/hR; hst=1.0/g*((aL+aR)/2.0+(uL-uR)/4.0)*((aL+aR)/2.0+(uL-uR)/4.0); ust=(uL+uR)/2.0+aL-aR; } //Two-Shock Riemann Solver// inline void TSRS(double &hst, double &ust, double hL, double hR, double qL, double qR) { double uL=qL/hL; double uR=qR/hR; TRRS(hst,ust,hL,hR,qL,qR); //EDPRS(hst,ust,hL,hR,qL,qR); double hcon=hst; hst=(gk(hst,hL)*hL+gk(hst,hR)*hR+uL-uR)/(gk(hst,hL)+gk(hst,hR)); ust=(uL+uR)/2.0+((hcon-hR)*gk(hcon,hR)-(hcon-hL)*gk(hcon,hL))/2.0; } //function for HLL// inline double qk(double hst, double hlr) { double qk=1.0; if(hst>hlr) qk=sqrt((hst+hlr)*hst/(hlr*hlr)/2.0); return qk; } //left wave estimation// inline double SLeft(double hst, double hL, double qL) { double uL=qL/hL; return uL-a(hL)*qk(hst,hL); } //right wave estimation// inline double SRight(double hst, double hR, double qR) { double uR=qR/hR; return uR+a(hR)*qk(hst,hR); } //flux for continuity equation// inline double Fluxcon(double h, double q) { return q; } //flux for momentum equation// inline double Fluxmom(double h, double q) { return q*q/h+g*h*h/2.0; } //hll flux// inline void HLLFlux(double FLR[], double hL, double hR, double qL, double qR) { double hst,ust; //estimastion of hst and ust// TRRS(hst,ust,hL,hR,qL,qR); //TSRS(hst,ust,hL,hR,qL,qR); //EDPRS(hst,ust,hL,hR,qL,qR); //wave speed estimation// double SL=SLeft(hst,hL,qL); double SR=SRight(hst,hR,qR); if(SL>=0) { FLR[0]=Fluxcon(hL,qL); FLR[1]=Fluxmom(hL,qL); } else if(SR<=0) { FLR[0]=Fluxcon(hR,qR); FLR[1]=Fluxmom(hR,qR); } else { FLR[0]=(SR*Fluxcon(hL,qL)-SL*Fluxcon(hR,qR)+SR*SL*(hR-hL))/(SR-SL); FLR[1]=(SR*Fluxmom(hL,qL)-SL*Fluxmom(hR,qR)+SR*SL*(qR-qL))/(SR-SL); } } inline void output(double h[], double z[], int Node, double dx) { stringstream ss; string name; ofstream fo; static int count=0; ss<<count; name=ss.str(); name="h_" + name + ".txt"; fo.open(name.c_str ()); for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { fo<<dx*float(i)<<" "<<h[i]+z[i]<<endl; } fo<<endl; fo<<endl; for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { fo<<dx*float(i)<<" "<<z[i]<<endl; } count+=1; } int main() { const int n=200;//number of cells const int Node=n+1; double L=1.0; double dx=L/double(n); double dt=0.0001; double TotalTime=2.0; int div=50;//for output double q[Node]; double h[Node]; double qn[Node]; double hn[Node]; double FL[2],FR[2]; double InithL=0.5; double InithR=1.0; double z[Node]; double I[Node]; double mn=0.01; //IC// for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { q[i]=0.0; h[i]=InithL; } for(int i=Node/3;i<Node*2/3;i++) { q[i]=0.0; h[i]=InithR; } //bottom// for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { z[i]=0.0; double a=0.1-3.0*(float(i)*dx-0.5)*(float(i)*dx-0.5); if(a>0.0) z[i]=a; z[i]=0.0; } //slope// for(int i=1;i<Node-1;i++) { I[i]=-(z[i]-z[i-1])/dx; } //at boundary// I[0]=-(z[1]-z[0])/dx; I[Node-1]=-(z[Node-1]-z[Node-2])/dx; //IC output// output(h,z,Node,dx); //time step// for(int k=1;double(k)*dt<=TotalTime;k++) { //inner cells// for(int i=1;i<Node-1;i++) { //left flux, between i-1 and i// HLLFlux(FL,h[i-1],h[i],q[i-1],q[i]); //right flux, between i and i+1// HLLFlux(FR,h[i],h[i+1],q[i],q[i+1]); hn[i]=h[i]-dt/dx*(FR[0]-FL[0]); qn[i]=q[i]-dt/dx*(FR[1]-FL[1])+dt*g*h[i]*(I[i]-mn*mn*q[i]*abs(q[i])/pow(h[i],10.0/3.0)); } //BC// HLLFlux(FL,h[Node-1],h[0],q[Node-1],q[0]); HLLFlux(FR,h[0],h[1],q[0],q[1]); hn[0]=h[0]-dt/dx*(FR[0]-FL[0]); qn[0]=q[0]-dt/dx*(FR[1]-FL[1])+dt*g*h[0]*(I[0]-mn*mn*q[0]*abs(q[0])/pow(h[0],10.0/3.0)); HLLFlux(FL,h[Node-2],h[Node-1],q[Node-2],q[Node-1]); HLLFlux(FR,h[Node-1],h[0],q[Node-1],q[0]); hn[Node-1]=h[Node-1]-dt/dx*(FR[0]-FL[0]); qn[Node-1]=q[Node-1]-dt/dx*(FR[1]-FL[1]);//+dt*g*h[Node-1]*(I[Node-1]-mn*mn*q[Node-1]*abs(q[Node-1])/pow(h[Node-1],10.0/3.0)); //update// for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { q[i]=qn[i]; h[i]=hn[i]; } //output// if(k%div==0) { output(h,z,Node,dx); cout<<"t="<<double(k)*dt<<endl; } } return 0; }
こちらもどうぞ
【浅水流方程式】HLL法でバンプ周りの流れを解いてみました 動画とC++コード付き
【浅水流方程式】サイトマップ(ここから関連記事が探せます)
http://mathlang.hatenablog.com/entry/2018/12/18/213650
今回は、HLL法(Harten, Lax, van Leer法)を用いてバンプ周りの流れを解いてみました。解いている方程式は、摩擦、勾配を考慮した1次元浅水流方程式(Shallow Water Equations)です。
領域の真ん中にバンプ(出っ張り、こぶ)を配置し、水がその上をどのように流れるか計算しています。
参考文献としてはToroの"Shock-Capturing Methods for Free-Surface Shallow Flows"のpp.179-181です。まさにバイブルです。波速を推定するための手法としては、Exact Depth Positivity Riemann Solver (EDPRS)、Two-Rarefaction Riemann Solver (TRRS)、Two-Shock Riemann Solver (TSRS) を選べるようになっています。

Shock-Capturing Methods for Free-Surface Shallow Flows
- 作者: Eleuterio F. Toro
- 出版社/メーカー: Wiley
- 発売日: 2001/03/23
- メディア: ハードカバー
- この商品を含むブログを見る
こちらが計算結果です。上の青い線が水深で、下の青い線が河床を表しています。
では計算コードです。といっても の更新式に項を足しただけです。
#include <iostream> #include <cmath> #include <fstream> #include <iomanip> #include <sstream> using namespace std; const double g=9.8; //celerity// inline double a(double h) { return sqrt(g*h); } //function for TRRS// inline double gk(double h0, double hlr) { return sqrt(g/2.0*(h0+hlr)/(h0*hlr)); } //Riemann Solver Based on Exact Depth Positivity// inline void EDPRS(double &hst, double &ust, double hL, double hR, double qL, double qR) { double aL=a(hL); double aR=a(hR); double uL=qL/hL; double uR=qR/hR; hst=(hL+hR)/2.0-(uR-uL)*(hL+hR)/4.0/(aL+aR); ust=(uL+uR)/2.0-(hR-hL)*(aL+aR)/(hL+hR); } //Two-Rarefaction Riemann Solver// inline void TRRS(double &hst, double &ust, double hL, double hR, double qL, double qR) { double aL=a(hL); double aR=a(hR); double uL=qL/hL; double uR=qR/hR; hst=1.0/g*((aL+aR)/2.0+(uL-uR)/4.0)*((aL+aR)/2.0+(uL-uR)/4.0); ust=(uL+uR)/2.0+aL-aR; } //Two-Shock Riemann Solver// inline void TSRS(double &hst, double &ust, double hL, double hR, double qL, double qR) { double uL=qL/hL; double uR=qR/hR; TRRS(hst,ust,hL,hR,qL,qR); //EDPRS(hst,ust,hL,hR,qL,qR); double hcon=hst; hst=(gk(hst,hL)*hL+gk(hst,hR)*hR+uL-uR)/(gk(hst,hL)+gk(hst,hR)); ust=(uL+uR)/2.0+((hcon-hR)*gk(hcon,hR)-(hcon-hL)*gk(hcon,hL))/2.0; } //function for HLL// inline double qk(double hst, double hlr) { double qk=1.0; if(hst>hlr) qk=sqrt((hst+hlr)*hst/(hlr*hlr)/2.0); return qk; } //left wave estimation// inline double SLeft(double hst, double hL, double qL) { double uL=qL/hL; return uL-a(hL)*qk(hst,hL); } //right wave estimation// inline double SRight(double hst, double hR, double qR) { double uR=qR/hR; return uR+a(hR)*qk(hst,hR); } //flux for continuity equation// inline double Fluxcon(double h, double q) { return q; } //flux for momentum equation// inline double Fluxmom(double h, double q) { return q*q/h+g*h*h/2.0; } //hll flux// inline void HLLFlux(double FLR[], double hL, double hR, double qL, double qR) { double hst,ust; //estimastion of hst and ust// TRRS(hst,ust,hL,hR,qL,qR); //TSRS(hst,ust,hL,hR,qL,qR); //EDPRS(hst,ust,hL,hR,qL,qR); //wave speed estimation// double SL=SLeft(hst,hL,qL); double SR=SRight(hst,hR,qR); if(SL>=0) { FLR[0]=Fluxcon(hL,qL); FLR[1]=Fluxmom(hL,qL); } else if(SR<=0) { FLR[0]=Fluxcon(hR,qR); FLR[1]=Fluxmom(hR,qR); } else { FLR[0]=(SR*Fluxcon(hL,qL)-SL*Fluxcon(hR,qR)+SR*SL*(hR-hL))/(SR-SL); FLR[1]=(SR*Fluxmom(hL,qL)-SL*Fluxmom(hR,qR)+SR*SL*(qR-qL))/(SR-SL); } } inline void output(double h[], double z[], int Node, double dx) { stringstream ss; string name; ofstream fo; static int count=0; ss<<count; name=ss.str(); name="h_" + name + ".txt"; fo.open(name.c_str ()); for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { fo<<dx*float(i)<<" "<<h[i]+z[i]<<endl; } fo<<endl; fo<<endl; for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { fo<<dx*float(i)<<" "<<z[i]<<endl; } count+=1; } int main() { const int n=200;//number of cells const int Node=n+1; double L=1.0; double dx=L/double(n); double dt=0.0001; double TotalTime=1.2; int div=20;//for output double q[Node]; double h[Node]; double qn[Node]; double hn[Node]; double FL[2],FR[2]; double InithL=0.2; double InithR=0.2; double z[Node]; double I[Node]; double mn=0.01; //IC// for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { q[i]=0.0; h[i]=InithL; } for(int i=Node/2;i<Node;i++) { q[i]=0.0; h[i]=InithR; } //bottom// for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { z[i]=0.0; double a=0.1-3.0*(float(i)*dx-0.5)*(float(i)*dx-0.5); if(a>0.0) z[i]=a; cout<<z[i]<<endl; } //slope// for(int i=1;i<Node-1;i++) { I[i]=-(z[i]-z[i-1])/dx; } //at boundary// I[0]=-(z[1]-z[0])/dx; I[Node-1]=-(z[Node-1]-z[Node-2])/dx; //IC output// output(h,z,Node,dx); //time step// for(int k=1;double(k)*dt<=TotalTime;k++) { //inner cells// for(int i=1;i<Node-1;i++) { //left flux, between i-1 and i// HLLFlux(FL,h[i-1],h[i],q[i-1],q[i]); //right flux, between i and i+1// HLLFlux(FR,h[i],h[i+1],q[i],q[i+1]); hn[i]=h[i]-dt/dx*(FR[0]-FL[0]); qn[i]=q[i]-dt/dx*(FR[1]-FL[1])+dt*g*h[i]*(I[i]-mn*mn*q[i]*abs(q[i])/pow(h[i],10.0/3.0)); } //BC// //left boundary// hn[0]=hn[1]; //qn[0]=qn[1]; qn[0]=0.5; //right boundary// hn[Node-1]=hn[Node-2]; //qn[Node-1]=qn[Node-2]; qn[Node-1]=0.5; //update// for(int i=0;i<Node;i++) { q[i]=qn[i]; h[i]=hn[i]; } //output// if(k%div==0) { output(h,z,Node,dx); cout<<"t="<<double(k)*dt<<endl; } } return 0; }
こちらもどうぞ
【語学リンク】ムヒカをスペイン語で読むためのリンク
ムヒカの名言集。和訳と解説付き。
ムヒカの演説。和訳と英訳、エスペラント訳付き。